• Overall there were 91 CyberTech deals in the first half of 2022 and the UK accounted for the most with 24 deals, a 26% share of total deals. Germany was second with 13 deals and France was third with 11 deals. Seed funding rounds were the most common funding type in Europe accounting for 36% of total CyberTech deals in the first six months of the year.
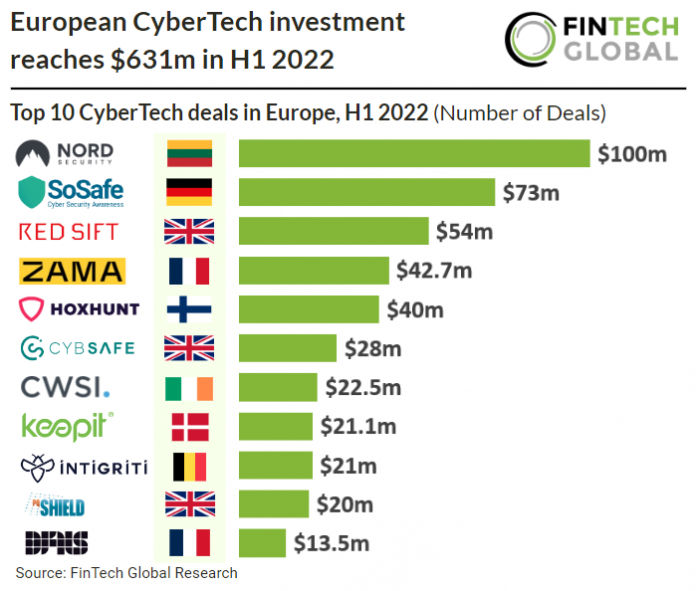
• Nord Security, which offers a comprehensive cybersecurity package against online hazards, was the largest CyberTech deal in H1 2022, raising $100m in their latest venture round, led by Novator, which gives Nord Security unicorn status at a $1.6bn valuation. The company will use the capital to expand its product suites while focusing on the growth of Surfshark, the consumer cybersecurity company Nord Security merged with in early 2022. Nord Security will also be working on R&D for their new platform features.
• The newest regulation that has gone into affect in Europe came from the EU’s Cybersecurity Act which came into force on 27th June 2019 and will apply in full across the EU from 28th June 2021. It has two main purposes: To give ENISA (the EU Agency for Network and Information Security) a permanent mandate; and to establish a European cyber security certification framework for ICT (information and communications technology) products, services and processes. The framework sets EU-wide parameters for the rules, technical requirements, standards and procedures surrounding risk-based certification schemes covering different categories of ICT products, processes and services.
The data for this research was taken from the FinTech Global database. More in-depth data and analytics on investments and companies across all FinTech sectors and regions around the world are available to subscribers of FinTech Global. ©2022 FinTech Global