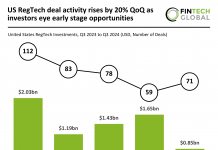
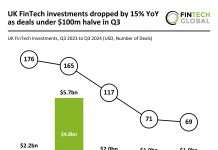
Graph databases and network analysis have become pivotal in the field of Anti-Money Laundering (AML), offering a sophisticated approach to understanding and disrupting financial networks. Unlike traditional relational databases that structure data linearly, graph databases excel in depicting the complex relationships between diverse entities. This ability is crucial in today’s landscape where financial criminals deploy intricate schemes to mask illicit activities.
Napier AI, an AI-powered anti-money laundering platform, recently explored graph databases and network analysis in AML.
Modelling Complex Networks of Transactions
AML processes involve mapping intricate webs of transactions, often with numerous intermediaries and connected entities. Graph databases are ideally suited for this task, as they naturally represent and visualise the relationships and shared characteristics across different nodes, it said. This provides compliance analysts with a clearer and more comprehensive understanding of suspicious activities, enhancing their ability to pinpoint and investigate anomalies.
Detection of Suspicious Patterns and Anomalies
Through network analysis, certain transaction patterns that typically indicate money laundering can be identified more easily. These include circular transactions, where funds are returned to the sender; smurfing, which involves breaking large transactions into smaller, less noticeable amounts; and the use of money mules to move illicit funds covertly. Although these patterns might mimic normal activity, graph algorithms aid in discerning genuine threats by evaluating centrality measures, community detection, and other sophisticated methods to filter out false positives.
Enhanced Entity Resolution
A key challenge in AML is the accurate identification of individuals or entities attempting to evade detection through the use of multiple identities or complex corporate structures. Graph databases enhance entity resolution by linking disparate data records that reference the same entity, such as shared addresses or similar contact details. This capability is critical for effective KYC practices and offers a more dynamic and holistic view of potential risks.
Read the full story here.
Keep up with all the latest FinTech news here
Copyright © 2024 FinTech Global